Classification of the main factors affecting CAC 40 performance<
Classification of the main factors affecting CAC 40 performance
CAC 40 is the performance index that has the most influence in the French economy.Founded in December 1987, this is a stock market index which brings together the 40 most important French actions within Euronext Paris.This is the main securities market in France, and the second largest market place in Europe after the London Stock Exchange in terms of market capitalization.For all those who wish to gauge the performance of companies within the fifth world economy and Europe, the CAC 40 is an excellent starting point.
Current factors affecting the CAC 40
You have to see the CAC 40 in the same way as the Dow Jones used on the US stock market.The index selects the main French shares classified by value and by market capitalization - more details in the rest of this article.The CAC 40 Tracker owes its name to the Company of Exchange Agents (CAC), the organization that launched and managed the Paris Stock Exchange at the beginning of the 19th century.
The relationship between exchange agents and financial exchanges dates back much further.Certain documents thus report a management of stock market transactions going up to the 16th century.Its approved brokers carried out commercial activities on the Paris Stock Exchange for centuries, until the dissolution of the CAC following the law of January 22, 1988 on the reform of the stock exchange.
The CAC was quickly replaced by the Company of French Stock Exchange, which was set up to monitor and manage the Paris Stock Exchange.This was the case until its merger with other leading European scholarships in Amsterdam, Brussels and Lisbon in the fall of 2000, which led to the training of the Euronext group.
The tradition of the CAC in French financial exchanges has however continued in the form of a new national index called CAC 40.We know him as a weighted indice according to the capitalization.The overall value of the index is influenced by the fluctuation of the prices of individual actions listed within the CAC 40.Shares that present the highest market capitalization are those that have the most influence on the entire index. Cela fonctionne de la même façon que d'autres indices boursiers nationaux connus tels que le FTSE 100 et le S&P 500.
The list of French companies included in the Euronext CAC 40 is determined each quarter by the index steering committee.This scientific council organizes assessment meetings of CAC 40 companies every three months, in order to classify their overall performance within Euronext Paris.Each title is classified according to its floating capitalization and the evolution of shares in the last 12 months of negotiations.The scientific council then selects the 40 most efficient companies, which form the Euronext CAC 40 index.This index provides a specific reference point for French companies, given that most of the titles included in CAC 40 are companies domiciled in France.
It is interesting to note here that the former president, Jacques Chirac, had mentioned during a speech in 2010 the fact that almost half (45 %) of all the shares listed in CAC 40 were held by foreign investors: a higher figure than any other major European index.This concretely means that a large number of these French companies are multinationals that do not focus exclusively on the internal market.
The first 10 CAC 40 companies
We offer below an overview of some of the main companies and industries listed on the stock market which are included in the list of CAC 40 when we write these lines.This should help you better understand why the CAC 40 index attracts international traders as much:
- LVMH (EPA : MC)Capitalisation boursière : 193,5 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 53,65 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019LVMH est l'abréviation de Louis Vuitton Moët Hennessy. Cette société est spécialisée dans une large gamme de produits de luxe, notamment dans le secteur de la mode, des cosmétiques et des vins et alcools fins. Bien que son siège social se trouve à Paris, LVMH possède un certain nombre de filiales qui opèrent dans le monde entier, gérant au total 75 célèbres marques. Tout ceci contribue au revenu annuel global de la société.
- L'Oréal (EPA : OR)Capitalisation boursière : 152,8 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 29,87 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019L'Oréal est une composante majeure de l'indice CAC 40. Depuis maintenant plus d'un siècle, la société, dont le siège social se trouve à Clichy, est l'entreprise de cosmétiques la plus influente au monde. Avec plus de 88 000 employés spécialisés dans les soins de la peau et des cheveux, ainsi que dans la parfumerie, ses filiales telles que Maybelline, Garnier et Lancôme sont des noms bien connus aux quatre coins du monde.
- Total SE (LON : TTA)Capitalisation boursière : 84,8 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 176,3 milliards de dollars en décembre 2019Mise en place après la fin de la Première Guerre mondiale, la société Total a été créée en mars 1924 sous le couvert de la « Compagnie Française des Pétroles » (CFP). Bien que la CFP, renommée Total en 1985, ait démarré en tant que compagnie pétrolière axée sur la France, elle a depuis acquis des participations dans de nombreuses entreprises et est aujourd'hui considérée comme l'un des sept « supermajors » parmi les compagnies pétrolières mondiales.
- Sanofi (EPA : SAN)Capitalisation boursière : 108,2 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 37,6 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019La société anonyme Sanofi a à l'origine été fondée en 1973 et, malgré sa fusion avec Aventis en 2004, la multinationale française continue de jouer les premiers rôles en matière de recherche et développement pharmaceutique, à la fois au niveau des médicaments délivrés sur ordonnance et en vente libre. Sanofi a travaillé à la phase 1 des essais cliniques d'un potentiel vaccin contre le COVID-19, lequel pourrait être autorisé pour une utilisation en cas d'urgence en 2021.
- Airbus (EPA : AIR)Capitalisation boursière : 53,9 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 70,4 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019L'intégration d'Airbus au CAC 40 n'est pas vraiment surprenante, étant donné que son siège social opérationnel se trouve à Toulouse et qu'il s'agit du plus grand constructeur d'avions au monde. L'activité principale de la compagnie, à savoir la construction d'avions civils, est menée sous la houlette de sa société française Airbus S.A.S. Ses actions ne sont pas uniquement négociées dans le cadre du CAC 40, elles sont également disponibles sur les bourses allemande et espagnole.
- Kering (EPA : KER)Capitalisation boursière : 61,8 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 15,9 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019Création de François Pinault, ce détaillant de produits de luxe s'est considérablement développé au cours des dernières décennies, acquérant des participations majoritaires dans certaines des plus grandes enseignes d'Europe, notamment Gucci et Yves Saint-Laurent. Aujourd'hui, Kering se concentre en particulier sur le développement durable ainsi que les produits de luxe. La société n'hésite pas à acquérir des marques dans le monde entier, avec notamment l'achat de la marque chinoise Qeelin en 2012 et le rachat de la marque britannique Christopher Kane en 2014.
- Hermès International (EPA : RMS)Capitalisation boursière : 72,9 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 6,88 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019Fondée en 1837 par Thierry Hermès, il s'agit de l'une des marques françaises de haute couture les plus respectées. Le magazine Forbes l'a classée au 33e rang parmi les marques les mieux cotées au niveau mondial en 2019. Il n'y a rien de surprenant à cela, si l'on considère le fait qu'Hermès possède également une participation de 35 % dans l'emblématique maison de haute couture Jean-Paul Gaultier.
- BNP Paribas (EPA : BNP)Capitalisation boursière : 44 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 55 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019Groupe bancaire français bénéficiant d'une influence mondiale, BNP Paribas est le plus grand de l'ensemble de la zone euro. Avec le Crédit Agricole et la Société Générale, BNP Paribas est l'une des trois banques françaises qui sont présentes sur la scène internationale. Aujourd'hui, elle opère dans 72 pays et se classe au huitième rang des banques mondiales en termes d'actifs globaux. BNP Paribas est listée sur Euronext Paris et l'indice Euro Stoxx 50, ainsi que sur le CAC 40.
- Air Liquide (EPA : AI)Capitalisation boursière : 64,9 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 21,9 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019Fruit d'un projet d'innovation de Georges Claude, le géant des gaz industriels Air Liquide a vu le jour au début du XXe siècle. Bien que son siège social soit toujours situé à Paris, Air Liquide possède également des divisions importantes dans le monde entier, notamment au Japon, aux États-Unis, en Chine et aux Émirats arabes unis. En termes de revenus annuels, le groupe est à présent le deuxième plus grand fournisseur de gaz industriels au monde.
- AXA (EPA : CS)Capitalisation boursière : 40,9 milliards d'euros en août 2020Revenus annuels : 124,9 milliards d'euros en décembre 2019Fondée il y a plus de deux siècles, cette entreprise de services financiers s'est considérablement développée au cours des 50 dernières années, principalement grâce à des acquisitions multiples, parmi lesquelles la Compagnie Parisienne de Garantie, le groupe Drouot et The Equitable. L'assureur est devenu AXA en 1999. À la fin de la dernière décennie, AXA était considérée comme l'une des multinationales les plus influentes et ce, grâce au contrôle exercé par ses sociétés sur la stabilité financière du monde entier.
A large number of the companies mentioned above are part of the CAC 40 from the start, due to their importance and their value for French, European and global economies.Of course, things have not always been easy for these companies and for CAC 40 as a whole.Since the commercial activities of these companies are carried out mainly outside France, they are often vulnerable to turbulence related to the economy, health and politics that shake Europe and the rest of the world.
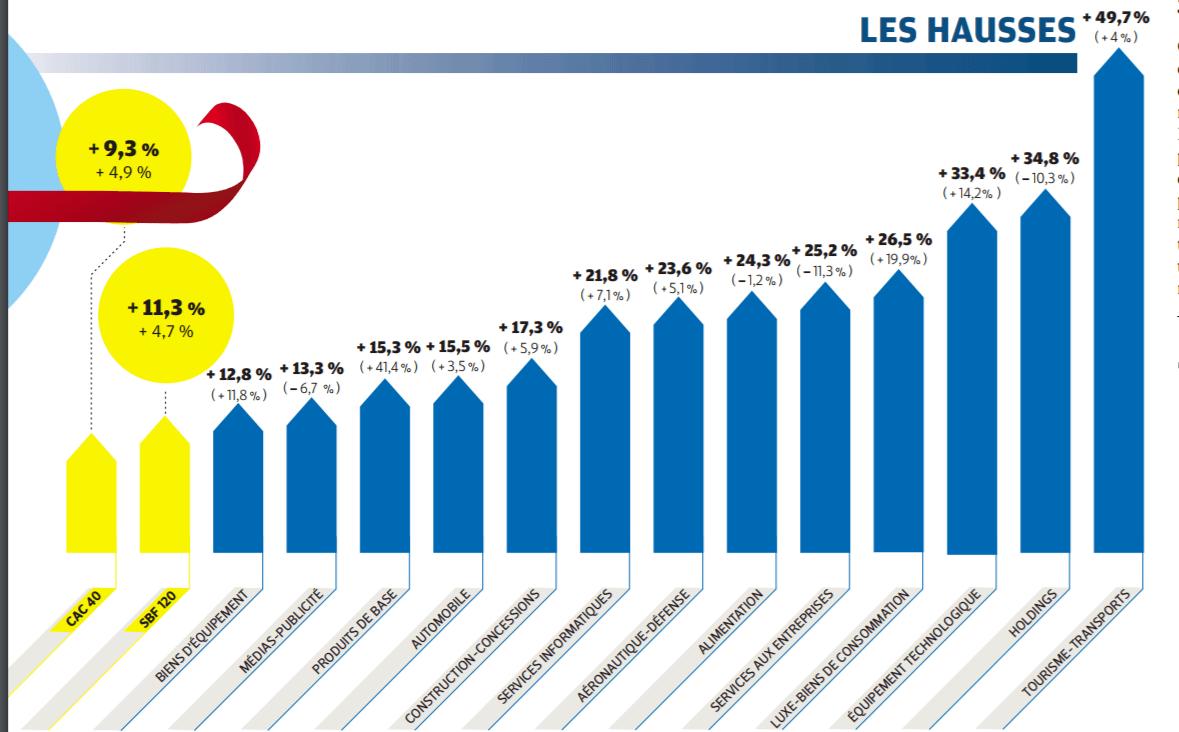
The following factors had a direct impact on the overall value of the CAC 40 during the 33 years of existence of the index:
Economic booms
When the national and global economy is doing well, the CAC 40 is doing well.The CAC 40 even reached its record level at the time of the Internet bubble in September 2000.The bubble has formed following the enormous financial speculation of investors within Internet companies, arising from the growing adoption of Internet technologies.The course of the CAC 40 followed the same trend as other major indices such as the Nasdaq Composite, many of the 40 largest multinationals listed on the Euronext Paris being capable of doing well, in the same way as theAmbitious young companies in American Silicon Valley.
It should also be noted that CAC 40 forecasts have been particularly influenced by the policies implemented by the European Central Bank (ECB).The ECB is different from other central banks such as the Bank of England because it defines monetary policy for the entire euro zone.Consequently, the variations of the euro can come to support or weaken the value of the CAC 40.A strong and competitive euro compared to other major currency pairs represents a boon for multinationals within CAC 40, allowing them to import more and at a lower cost from countries outside the euro zone.Conversely, a lower euro increases the competitiveness of French exports and those from the euro zone.
Political earthquakes
Financial markets and multinationals appreciate stability.It is the watchword for most upturn markets.Consequently, when a country goes through a period of political instability or faces a major potential change at its head, it is not surprising to see the forecasts of the CAC 40 subject to uncertainty and volatility.
When we talk about political earthquake, we mainly refer to a marked change in ideology;In this case, we think of the risk that the fiscal or monetary policy of a political party is modified by the opposite program of another party.The 2017 presidential election in France, which ended in a duel between Emmanuel Macron and Marine Le Pen, represents the most speaking example of the major impact that the policy of CAC 40 can have.In this case, the financial markets took a while to accept the fact that Ms. Le Pen, far-right candidate, had a real chance of becoming the next president of France.As the popularity of Marine Le Pen increased, the CAC 40 index became more unstable, less efficient and extremely low compared to the German Dax index.
Reason: Marine Le Pen's political vision was, in the long term, to bring France out of the European Union and to adopt a more nationalist approach to the French economy.If such a scenario were to come true, a market revolt was to be feared, the multinationals of the CAC 40 then faced more bureaucracy in the context of new trade relations with the rest of the EU.But it was finally Emmanuel Macron who won the election, which led to a new period of stability of the CAC 40.
Unforeseen national and international crises
The first major international crisis that marked the history of CAC 40 is undoubtedly the 2008 global recession.In 1929, at the time when Wall Street's American crash had hit North America hard, the Paris Stock Exchange had been much less affected;This had clearly shown how independently the two stock markets operated almost a century ago.If we are now advancing in 2008, we realize that the collapse of Lehman Brothers had much more important repercussions on the course of CAC 40, because the markets are much more integrated due to the growing number of French multinationals.
How to replace a broken floor #tile in 7 simple steps! ---> https://t.co/hQlROWnXak #Gerasa #DIY #LoveJo #Grout https://t.CO/1JAYV3IQ2X
— Gerasa Mon Nov 05 08:33:06 +0000 2018
We also have to mention the repercussions that the world pandemic of COVVI-19 on the CAC 40 tracker at present.In fact, the CAC 40 course fell more strongly during the first weeks of confinement imposed by the French government to combat the coronavirus only after the collapse of Lehman Brothers in September 2008.The prospects and forecasts of profit having been considerably revised downwards by a series of companies listed at CAC 40, it is not surprising that the index was finally so bad.
The COVVI-19 pandemic also played a role in this year's oil crisis: the international demand for fuel and crude oil collapsed.With containment measures, production has stopped, while global slowdown in air transport has also eroded confidence in the sector.The sharp drop in oil and gas prices has hit total hardly, one of the largest CAC 40 companies in terms of market capitalization;It is therefore easy to understand why international crises affecting specific sectors can also vary the CAC 40.
How important is the impact of these external factors?
Among the three main external factors to which the Euronext CAC 40 is sensitive, which is most likely to have a long -term negative impact on the index?We have classified below the impact of each external factor on the CAC 40 index, of the one who has the least influence to the one who has the most.
1.Political earthquakes (the least influence)
The way in which the French economy must be managed: this is one of the most discussed points with the approach of a presidential election in France.This is no doubt, investors in the main French multinationals within the CAC 40 consult the respective political programs of candidates in order to decide their next investment.The result of a political election can often mark a turning point for the future of stock market indices such as the CAC 40.
We have already mentioned the way in which the possibility of a far-right nationalist president, in this case Marine Le Pen, had resulted in great uncertainty among the multinationals of CAC 40;But what about the impact of Emmanuel Macron's victory in the May 2017 election?
Before the first round of this 2017 election, an influential survey organization predicted that centrist candidate Emmanuel Macron was the one who was most likely to take it.Several weeks before this announcement, we heard that the Eurosceptics Marine Le Pen and Jean-Luc Mélenchon collected more and more support throughout the country.The biggest fear on the financial markets was to see a confrontation between Le Pen and Mélenchon on May 7, which would have led to a major transfer of the actions of the banks as well as the State obligations.
During the two weeks that surrounded the face-to-face between M.Macron and the leader of the National Front, Marine Le Pen, CAC 40 jumped 6 %, to reach its highest level in nine years.He also took a percentage point on Emmanuel Macron's victory day.However, the positivity that surrounded the CAC 40 was short -lived, the French actions then stagnating because we were betting on the probable incapacity of M.Macron to implement his reform program.
More recently, the CAC 40 index increased by 2.4 % between November 3 and 4, 2020, at the announcement of Joe Biden's victory in the American presidential election, combined with good news surrounding the vaccine ofPfizer.With several French multinationals present in the United States, the new approach to the center-left administration to combat the coronavirus crisis will help these brands regain foot.However, the increase in CAC 40 is also due to the dead end of the congress, which prevents Democrats from being able to fully implement their series of new tax and regulatory proposals.
2.Unforeseen national and international crises
The Covid-19 pandemic represents one of the world's largest challenges in a century.The necessary containment measures that have been taken inevitably led to a recession in 2020.In France alone, the OFCE believes that the first national confinement has resulted in a 32 % drop in GDP.In February 2020, the Euronext CAC 40 reached heights of 6,111.When President Macron was forced to announce national confinement a month later, the 40 main French companies had lost around 39 % of their value.
On March 12, 2020, we attended the strongest fall in the history of the Paris Stock Exchange, 566 points.In fact, the initial fall in the value of the CAC 40 index was stronger than that which followed the collapse of Lehman Brothers who had triggered the 2008 global recession.Although the short-term impact of the COVVI-19 in the CAC 40 ranking was more marked than the 2008 recession, the reality is that it is a health and economic crisis rather than abanking crisis.
According to data from the OFCE, profit prospects within companies listed at CAC 40 for 2021 have been reduced by 13.4 % between February and May 2020.However, the CAC 40 index according to Boursorama and other financial sources dropped no less than 39 % at a time during this period, a sign of an excessive reaction on the market.At the time, coronavirus was a new disease and vaccines still seemed far away.
What is more, the drop in the index was also linked to additional geopolitical turbulence, in particular the collapse of prices in the petroleum industry, which saw the price of total action decrease by more than half, passingfrom € 50 in January to 21 € in mid-March.
Like the price of total action, the CAC 40 index has shown signs of recovery in recent months, mainly due to the positive prospects for effective vaccines available en masse by the end of 2020 and discussions on a returnto a normal life by the middle of next year.The index rebounded from its lowest level of 3,754 in March at 5,476 on November 19: a resumption of around 31 % of the overall value of the index.
3.Economic and recession boom (most influence)
Over the years, the course of the CAC 40 index has evolved similarly to other major stock market indices from around the world, in particular the German Dax and the FTSE 100 British.All the main clues experienced exponential growth at the start of the new millennium, carried by a wave of technical automation and the overall emergence of the Internet.Between 1999 and 2000, the Euronext CAC 40 increased by 40 %, reaching its highest level to 6,922 in July 2000.
Despite the enormous positive effect that the Internet boom had, the famous "Internet bubble" broke out in 2001, causing the collapse of many technological values listed in clues such as the American Nasdaq.Even well -established advanced technology giants such as Intel have lost about four -fifths of their value when the bubble exploded.CAC 40 also felt the effects by ricochet.This, associated with the repercussions of terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 in New York, led to a decline in CAC 40 of more than 38 %.
In the United Kingdom, the FTSE 100 index dropped by 31.3 % when the 2008 great recession struck.The CAC 40 followed the same path, recording an even more damaging drop of 43 % in 2008 - its worst performance during its 20 years of existence.Stock values have lost billions of dollars, including CAC 40 shares.LVMH saw the course of action decrease by half at the end of 2008.
What are the biggest problems that have ever affected the French economy?
To allow you to have a global vision of the French economy and the CAC 40 index since its launch in 1987, we have prepared a chronology of key events that have had an influence on the drop or the rise of the CAC 40as well as on the most important multinationals in France:
The sharp drop in CAC 40 was also due to the global oil crisis which followed the first confinement linked to the COVVI-19.Fortunately, the delightful perspective of several vaccines against the coronavirus in 2021 and a return to a more normal life helped the French multinationals to plan the next 12 months with more certainties.In November 2020, the CAC 40 recovered approximately 80 % of the lost value in March.


 Tags:
Tags: Prev
Prev







